搜索进阶 dfs&bfs&迭代加深&A*算法
剪枝优化
优化搜索顺序
排除等效冗余
可行性剪枝
最优性剪枝
记忆化搜索
常数优化
今日战况
前言 我个人感觉我的搜索应该还是差不多的,但是今天的题目让我觉得我的剪枝方面的水平还有待提升,以及自己的构造能力不强,有时候在脑子里面能想出来一些东西,但是无法马上构思出代码,还得想亿会才能(也可能想不出来)。
部分题目题解 C题: Soduku (最简单版本的) 题目传送门
题目
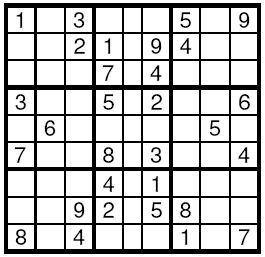
Sudoku is a very simple task. A square table with 9 rows and 9 columns is divided to 9 smaller squares 3x3 as shown on the Figure. In some of the cells are written decimal digits from 1 to 9. The other cells are empty. The goal is to fill the empty cells with decimal digits from 1 to 9, one digit per cell, in such way that in each row, in each column and in each marked 3x3 subsquare, all the digits from 1 to 9 to appear. Write a program to solve a given Sudoku-task.
Input
The input data will start with the number of the test cases. For each test case, 9 lines follow, corresponding to the rows of the table. On each line a string of exactly 9 decimal digits is given, corresponding to the cells in this line. If a cell is empty it is represented by 0.
Output
For each test case your program should print the solution in the same format as the input data. The empty cells have to be filled according to the rules. If solutions is not unique, then the program may print any one of them.
Sample Input
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 1 103000509 002109400 000704000 300502006 060000050 700803004 000401000 009205800 804000107
Sample Output
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 143628579 572139468 986754231 391542786 468917352 725863914 237481695 619275843 854396127
题目大意 有t个测试样例,每个样例都有一个9*9的数独,里面的0表示未确定的数,编程写这个数独,输出写好之后的数独。
思路 暴力的话就是用搜索遍历每一行每一个位置,枚举每一个可能的结果,直到得到结果。
此题数据比较水,暴力就直接能AC。
代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 #include <cstdio> #include <algorithm> #include <vector> #include <queue> #include <stack> #include <cstring> #define Inf 0x3f3f3f3f using namespace std;typedef pair<int ,int > P;typedef long long LL;const int MAXX=6005 ;const double eps=0.0000001 ;int a[10 ][10 ],belong[10 ][10 ];bool r[10 ][10 ],c[10 ][10 ],d[10 ][10 ],can;void output () for (int i=1 ;i<=9 ;++i){ for (int j=1 ;j<=9 ;++j) printf ("%d" ,a[i][j]); printf ("\n" ); } } void dfs (int jj,int kk) if (can) return ; if (a[jj][kk]){ if (kk<9 ) dfs (jj,kk+1 ); else if (jj<9 ) dfs (jj+1 ,1 ); else { output (); can=true ; } return ; } for (int i=1 ;i<=9 ;++i){ if (r[jj][i]||c[kk][i]||d[belong[jj][kk]][i]) continue ; a[jj][kk]=i; r[jj][i]=c[kk][i]=d[belong[jj][kk]][i]=true ; if (kk<9 ) dfs (jj,kk+1 ); else if (jj<9 ) dfs (jj+1 ,1 ); else { output (); can=true ; return ; } if (can) return ; a[jj][kk]=0 ; r[jj][i]=c[kk][i]=d[belong[jj][kk]][i]=false ; } } void solve_it () for (int i=1 ;i<=9 ;++i){ char jj; getchar (); for (int j=1 ;j<=9 ;++j){ scanf ("%c" ,&jj); a[i][j]=jj-'0' ; if (a[i][j]!=0 ){ r[i][a[i][j]]=true ; c[j][a[i][j]]=true ; d[belong[i][j]][a[i][j]]=true ; } } } can=false ; dfs (1 ,1 ); for (int i=1 ;i<=9 ;++i) for (int j=1 ;j<=9 ;++j){ a[i][j]=0 ; r[i][j]=c[i][j]=d[i][j]=false ; } } int main () for (int i=1 ;i<=9 ;++i) for (int j=1 ;j<=9 ;++j) belong[i][j]=(i-1 )/3 *3 +(j-1 )/3 +1 ; int t;scanf ("%d" ,&t); while (t--) solve_it (); return 0 ; }
D题: Soduku (变态数据版本的)(未做出来) 题目传送门
题目
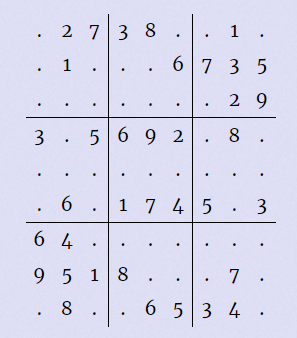
In the game of Sudoku, you are given a large 9 × 9 grid divided into smaller 3 × 3 subgrids. For example,
Given some of the numbers in the grid, your goal is to determine the remaining numbers such that the numbers 1 through 9 appear exactly once in (1) each of nine 3 × 3 subgrids, (2) each of the nine rows, and (3) each of the nine columns.
Input
The input test file will contain multiple cases. Each test case consists of a single line containing 81 characters, which represent the 81 squares of the Sudoku grid, given one row at a time. Each character is either a digit (from 1 to 9) or a period (used to indicate an unfilled square). You may assume that each puzzle in the input will have exactly one solution. The end-of-file is denoted by a single line containing the word “end”.
Output
For each test case, print a line representing the completed Sudoku puzzle.
Sample Input
1 2 3 .2738..1..1...6735.......293.5692.8...........6.1745.364.......9518...7..8..6534. ......52..8.4......3...9...5.1...6..2..7........3.....6...1..........7.4.......3. end
Sample Output
1 2 527389416819426735436751829375692184194538267268174593643217958951843672782965341 416837529982465371735129468571298643293746185864351297647913852359682714128574936
题目大意 和上道题大意一样,输入一个数独,输出填充完整的数独。但是测试数据要比C题离谱的多。
思路 各种优化
我目前的代码只进行了搜索顺序的优化,常熟优化还没学会。
附上进行了搜索顺序优化的代码。
代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 #include <cstdio> #include <algorithm> #include <vector> #include <queue> #include <stack> #include <cstring> #include <iostream> #include <string> #define Inf 0x3f3f3f3f using namespace std;typedef pair<int ,int > P;typedef long long LL;const int MAXX=6005 ;const double eps=0.0000001 ;struct row { int id,num; }cnt[10 ]; int a[10 ][10 ],belong[10 ][10 ],rate[10 ];string s; bool r[10 ][10 ],c[10 ][10 ],d[10 ][10 ],can;bool cmp (row jj,row kk) return jj.num<kk.num;}void output () for (int i=1 ;i<=9 ;++i){ for (int j=1 ;j<=9 ;++j) printf ("%d" ,a[i][j]); } printf ("\n" ); } void dfs (int jj,int kk) if (can) return ; if (a[jj][kk]){ if (kk<9 ) dfs (jj,kk+1 ); else if (rate[jj]<9 ) dfs (cnt[rate[jj]+1 ].id,1 ); else { output (); can=true ; } return ; } for (int i=1 ;i<=9 ;++i){ if (r[jj][i]||c[kk][i]||d[belong[jj][kk]][i]) continue ; a[jj][kk]=i; r[jj][i]=c[kk][i]=d[belong[jj][kk]][i]=true ; if (kk<9 ) dfs (jj,kk+1 ); else if (rate[jj]<9 ) dfs (cnt[rate[jj]+1 ].id,1 ); else { output (); can=true ; return ; } if (can) return ; a[jj][kk]=0 ; r[jj][i]=c[kk][i]=d[belong[jj][kk]][i]=false ; } } void solve_it () int p=-1 ; for (int i=1 ;i<=9 ;++i){ cnt[i].id=i; cnt[i].num=0 ; for (int j=1 ;j<=9 ;++j){ if (s[++p]=='.' ){ a[i][j]=0 ; ++cnt[i].num; continue ; } a[i][j]=s[p]-'0' ; r[i][a[i][j]]=true ; c[j][a[i][j]]=true ; d[belong[i][j]][a[i][j]]=true ; } } sort (cnt+1 ,cnt+10 ,cmp); for (int i=1 ;i<=9 ;++i) rate[cnt[i].id]=i; can=false ; dfs (cnt[1 ].id,1 ); for (int i=1 ;i<=9 ;++i) for (int j=1 ;j<=9 ;++j){ a[i][j]=0 ; r[i][j]=c[i][j]=d[i][j]=false ; } } int main () for (int i=1 ;i<=9 ;++i) for (int j=1 ;j<=9 ;++j) belong[i][j]=(i-1 )/3 *3 +(j-1 )/3 +1 ; while (true ){ cin>>s; if (s=="end" ) break ; solve_it (); } return 0 ; }
F题: 靶形数独 题目传送门
这里就不放题目了,思路和上面的数独的题一样,通过优化搜索顺序即可AC
枚举出每种可能的最终结果,取最大值即可
代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 #include <cstdio> #include <algorithm> #include <vector> #include <queue> #include <stack> #include <cstring> #include <iostream> #include <string> #define Inf 0x3f3f3f3f using namespace std;typedef pair<int ,int > P;typedef long long LL;const int MAXX=6005 ;const double eps=0.0000001 ;struct row { int id,num; }cnt[10 ]; int a[10 ][10 ],belong[10 ][10 ],rate[10 ],ans;bool r[10 ][10 ],c[10 ][10 ],d[10 ][10 ];bool cmp (row jj,row kk) return jj.num<kk.num;}void output () for (int i=1 ;i<=9 ;++i){ for (int j=1 ;j<=9 ;++j) printf ("%d " ,a[i][j]); } printf ("\n" ); } int getans () int re=10 *a[5 ][5 ]; for (int i=1 ;i<=4 ;++i){ int st=5 -i,en=5 +i; int fen=10 -i; for (int j=st;j<=en;++j){ re+=a[st][j]*fen; re+=a[en][j]*fen; } for (int j=st+1 ;j<en;++j){ re+=a[j][st]*fen; re+=a[j][en]*fen; } } return re; } void dfs (int jj,int kk) if (a[jj][kk]){ if (kk<9 ) dfs (jj,kk+1 ); else if (rate[jj]<9 ) dfs (cnt[rate[jj]+1 ].id,1 ); else { ans=max (ans,getans ()); } return ; } for (int i=1 ;i<=9 ;++i){ if (r[jj][i]||c[kk][i]||d[belong[jj][kk]][i]) continue ; a[jj][kk]=i; r[jj][i]=c[kk][i]=d[belong[jj][kk]][i]=true ; if (kk<9 ) dfs (jj,kk+1 ); else if (rate[jj]<9 ) dfs (cnt[rate[jj]+1 ].id,1 ); else { ans=max (ans,getans ()); } a[jj][kk]=0 ; r[jj][i]=c[kk][i]=d[belong[jj][kk]][i]=false ; } } void solve_it () for (int i=1 ;i<=9 ;++i){ cnt[i].id=i; cnt[i].num=0 ; for (int j=1 ;j<=9 ;++j){ scanf ("%d" ,&a[i][j]); if (a[i][j]==0 ){ ++cnt[i].num; continue ; } r[i][a[i][j]]=true ; c[j][a[i][j]]=true ; d[belong[i][j]][a[i][j]]=true ; } } sort (cnt+1 ,cnt+10 ,cmp); for (int i=1 ;i<=9 ;++i) rate[cnt[i].id]=i; ans=-1 ; dfs (cnt[1 ].id,1 ); printf ("%d\n" ,ans); } int main () for (int i=1 ;i<=9 ;++i) for (int j=1 ;j<=9 ;++j) belong[i][j]=(i-1 )/3 *3 +(j-1 )/3 +1 ; solve_it (); return 0 ; }
总结 今天的搜索进阶听课和写题都挺有收获,知道了搜索的各种优化思路,以及了解到了迭代加深的思路,并成功依此A题。
今天先总结这三道题,明天再总结其他题目